flap reconstruction
overview
- Flap reconstruction (also called tissue-based reconstruction) is a procedure that involves moving healthy, live tissue from one location on your body to another. Usually this live tissue is moved to areas that have lost skin, fat, muscle movement, and/or skeletal support.
- Flap surgery can be used for procedures, such as breast reconstruction or trunk and extremity reconstruction. Doctors may also use flap surgery to help them reconstruct facial features or nerves.
- Dr Shilpi Sharma Best Flap Surgery Doctor In Gurgaon.
TYPES OF FLAP RECONSTRUCTION
There are several different types of flap reconstruction surgery. These include the following:
- Local flap—A local flap is located next to a wound; the skin tissue remains attached at one end so that the blood supply can keep flowing through that piece of skin.
- Regional flap—This uses a section of tissue that is attached by a specific blood vessel.
- Bone/soft tissue flap—This type of flap is often used when bone and the overlying skin are moved to a new location.
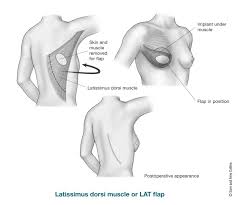
- Musculocutaneous flap (muscle and skin flap)—This type of flap is often used when the area to be covered needs more bulk and an increased blood supply. This type of flap is often used to rebuild a breast after a mastectomy (breast removal surgery).
- Microvascular free flap—This involves detaching and reattaching skin and blood vessels from one area of the body to another area. Doctors use microsurgery to reattach the blood vessels.
- turning blue or black
- feeling cool to the touch
- developing open wounds
- If there’s a loss of blood flow in the flap during the first few days after the initial surgery, your plastic surgeon may be able to save the flap by revising the blood vessel connections using microsurgery. Another possibility is that your surgeon might remove the flap and replace it with a flap of tissue from another part of your body or with an implant within a short timeframe. But if most or all of the flap has developed necrosis, usually your surgeon will just remove the flap and allow the area to heal. This is known as a “complete flap failure.”
- If you originally had a delayed reconstruction (when the reconstruction surgery takes place some period of time after the mastectomy), you’ll lose some breast skin that was part of the transplanted flap when the flap is removed. If you had immediate reconstruction (when the mastectomy and reconstruction are done at the same time), the flap was placed beneath the existing breast skin so you’ll be less likely to lose some skin when it is removed.
- A few months after the surgery to remove the flap, depending on your individual situation, you may be able to have your breast reconstructed again using a flap of tissue or an implant. If you want a flap surgery, you’ll need to work with your surgeon to identify a new donor site on your body for the tissue flap. Once you’ve already taken tissue from a particular donor site, such as the buttocks, inner thighs, or belly, it can’t be used again for reconstruction. To have your breast reconstructed with an implant after a complete flap failure, you need to have enough surviving skin and soft tissue to cover the implant. A tissue flap may be a better option if you lost a significant amount of skin and soft tissue.